Introduction to Green Building Materials
What Are Green Building Materials?
Green building materials, also known as eco-friendly construction materials, are materials that are both environmentally sustainable and resource-efficient throughout their life cycle. From the extraction of raw materials to their production, use, and disposal, green building materials aim to minimize environmental impact.
Importance of Using Green Building Materials
Using green building materials is crucial for reducing the carbon footprint of construction projects. These materials not only help in conserving natural resources but also promote healthier living spaces by reducing pollution and waste. The use of eco-friendly materials is a key component of sustainable building practices.
Benefits of Eco-Friendly Construction Materials
Environmental Benefits
One of the primary benefits of using green building materials is the positive impact on the environment. These materials help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, conserve natural resources, and decrease the amount of waste that ends up in landfills. Additionally, many eco-friendly materials are sourced from renewable resources, making them a sustainable choice for long-term use.
Health and Safety Benefits
Green building materials often have lower levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which can contribute to indoor air pollution and adverse health effects. By choosing materials that are free from harmful chemicals, builders can create healthier indoor environments for occupants. This is especially important for homes, schools, and workplaces where people spend a significant amount of time.
Types of Green Building Materials
Recycled Materials
Recycled materials are an excellent choice for eco-friendly construction. These materials include recycled steel, recycled wood, and recycled glass. Using recycled materials helps reduce the demand for new raw materials and minimizes waste.
Renewable Materials
Renewable materials are those that can be replenished naturally over a short period. Examples include bamboo, cork, and straw. These materials are sustainable because they grow quickly and can be harvested without causing long-term damage to the environment.
Innovative Green Building Materials
Hempcrete
Hempcrete is a bio-composite material made from the inner woody core of the hemp plant mixed with a lime-based binder. It is lightweight, durable, and provides excellent thermal and acoustic insulation. Hempcrete is also carbon-negative, meaning it absorbs more CO2 than it emits during its life cycle.
Mycelium
Mycelium is the root structure of mushrooms, which can be used to create a biodegradable and sustainable building material. Mycelium-based products are lightweight, fire-resistant, and have excellent insulating properties. This innovative material is also compostable, making it an environmentally friendly option.
Sustainable Wood Options
Bamboo
Bamboo is one of the most sustainable building materials available. It grows rapidly, reaching maturity in just a few years, and can be harvested without killing the plant. Bamboo is strong, durable, and can be used for a variety of construction purposes, from flooring to structural support.
Reclaimed Wood
Reclaimed wood is wood that has been salvaged from old buildings, barns, and other structures. It is an eco-friendly option because it repurposes existing materials, reducing the need for new wood. Reclaimed wood also adds character and a sense of history to a building project.
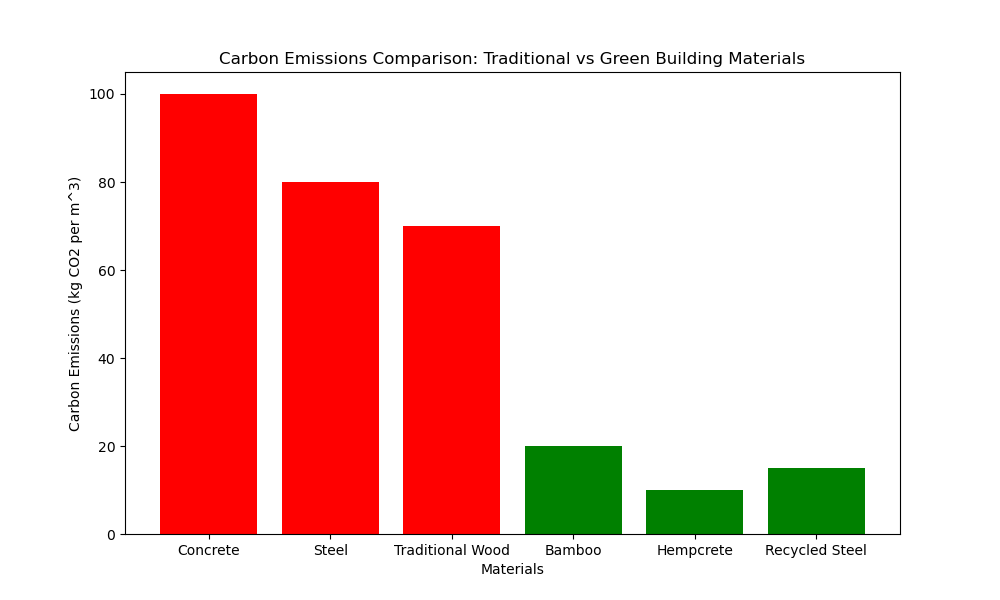
Green Insulation Materials
Cellulose Insulation
Cellulose insulation is made from recycled paper products, primarily newspaper. It is treated with fire retardants to ensure safety and provides excellent thermal and acoustic insulation. Cellulose insulation is an environmentally friendly option because it diverts waste paper from landfills and has a lower environmental impact compared to traditional insulation materials.
Sheep’s Wool Insulation
Sheep’s wool is a natural and renewable insulation material. It is highly effective at regulating temperature and humidity, providing a comfortable indoor environment. Sheep’s wool insulation is also biodegradable and has a low environmental impact.
Eco-Friendly Roofing Materials
Cool Roofs
Cool roofs are designed to reflect more sunlight and absorb less heat than standard roofs. They are typically made from highly reflective materials such as metal or white tiles. Cool roofs can reduce energy consumption by lowering the need for air conditioning, especially in hot climates.
Green Roofs
Green roofs, also known as living roofs, are covered with vegetation and soil. They provide numerous environmental benefits, including improved air quality, reduced stormwater runoff, and increased biodiversity. Green roofs also help insulate buildings, reducing energy costs.
Sustainable Flooring Options
Cork Flooring
Cork is a renewable material harvested from the bark of cork oak trees. It is durable, comfortable underfoot, and has natural insulating properties. Cork flooring is also hypoallergenic and resistant to mold and mildew, making it a healthy choice for indoor environments.
Recycled Rubber Flooring
Recycled rubber flooring is made from used tires and other rubber products. It is a durable and resilient flooring option that can withstand heavy use. Using recycled rubber helps reduce waste and the environmental impact of manufacturing new materials.
Eco-Friendly Paints and Finishes
Low-VOC Paints
Low-VOC (volatile organic compounds) paints are formulated to have fewer harmful chemicals, reducing indoor air pollution and potential health risks. These paints are available in a wide range of colors and finishes, making them a versatile and eco-friendly choice for any building project.
Natural Finishes
Natural finishes, such as linseed oil and beeswax, are made from renewable resources and are free from synthetic chemicals. They provide a safe and sustainable option for protecting and enhancing the appearance of wood and other materials.
Energy-Efficient Windows and Doors
Double-Glazed Windows
Double-glazed windows have two panes of glass with a space between them, which acts as an insulating barrier. This design helps reduce heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer, improving energy efficiency and comfort.
Insulated Doors
Insulated doors are designed to reduce heat transfer and improve energy efficiency. They are typically made with a core of insulating material, such as foam, and a durable outer shell. Insulated doors can help lower energy bills and create a more comfortable indoor environment.
Sustainable Landscaping Materials
Permeable Paving
Permeable paving materials, such as porous concrete and permeable pavers, allow water to pass through them, reducing stormwater runoff and promoting groundwater recharge. These materials help manage rainwater sustainably and reduce the risk of flooding.
Native Plants
Using native plants in landscaping is an eco-friendly choice because they are adapted to the local climate and soil conditions. Native plants require less water, fertilizer, and maintenance, making them a sustainable option for creating beautiful and resilient landscapes.
Water-Efficient Plumbing Fixtures
Low-Flow Toilets
Low-flow toilets use significantly less water per flush compared to traditional toilets. They are designed to provide effective flushing while conserving water, helping to reduce water consumption and lower utility bills.
Water-Saving Showerheads
Water-saving showerheads are designed to use less water while maintaining a comfortable flow. These fixtures can reduce water usage by up to 50%, making them an important part of any green building project.
Eco-Friendly Building Practices
Passive Solar Design
Passive solar design involves orienting a building and its windows to maximize natural light and heat from the sun. This design strategy can reduce the need for artificial lighting and heating, lowering energy consumption and improving comfort.
Modular Construction
Modular construction involves building sections of a structure off-site in a controlled environment, then transporting and assembling them on-site. This method reduces waste, minimizes site disturbance, and can shorten construction time, making it a more sustainable building practice.
Sustainable Building Certifications
LEED Certification
LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) is a widely recognized certification program for green buildings. Buildings earn points for various sustainable practices, such as using green building materials, improving energy efficiency, and reducing water consumption. LEED certification is a mark of excellence in sustainable building.
WELL Building Standard
The WELL Building Standard focuses on the health and well-being of building occupants. It includes criteria for air quality, water quality, lighting, and other factors that affect human health. Buildings that meet these criteria can earn WELL certification, demonstrating a commitment to creating healthy indoor environments.
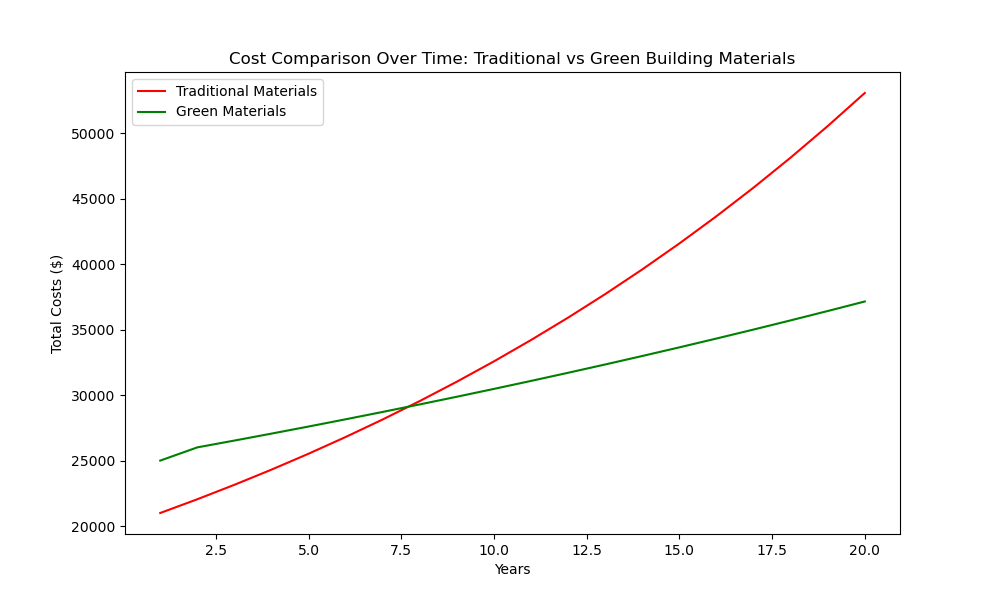
Cost Considerations for Green Building Materials
Initial Costs vs. Long-Term Savings
While green building materials may have higher upfront costs compared to traditional materials, they often provide long-term savings through reduced energy and water consumption, lower maintenance costs, and improved durability. Investing in eco-friendly materials can lead to significant financial benefits over the life of a building.
Incentives and Rebates
Many governments and organizations offer incentives and rebates for using green building materials and practices. These programs can help offset the initial costs and make sustainable building more affordable. Builders and homeowners should explore available incentives to maximize their savings.
Key Points Summary
- Green building materials help reduce environmental impact and promote sustainable construction.
- Examples of innovative materials include hempcrete and mycelium.
- Sustainable wood options like bamboo and reclaimed wood offer durability and eco-friendliness.
- Energy-efficient solutions such as double-glazed windows and insulated doors improve building performance.
- Incentives and rebates can make the adoption of green building materials more financially viable.
Eco-Friendly Concrete Alternatives
Fly Ash Concrete
Fly ash is a byproduct of coal combustion that can be used as a partial replacement for cement in concrete. Using fly ash reduces the need for cement, which is energy-intensive to produce, and helps divert waste from landfills. Fly ash concrete is strong, durable, and has a lower environmental impact.
Geopolymer Concrete
Geopolymer concrete is made from industrial byproducts such as fly ash and slag, mixed with an alkaline activator. This type of concrete has a lower carbon footprint compared to traditional Portland cement concrete and offers excellent durability and resistance to chemicals.
Green Building Materials for Interiors
Recycled Glass Countertops
Recycled glass countertops are made from post-consumer glass, such as bottles and windows, combined with a binder. These countertops are available in a variety of colors and patterns, offering a unique and sustainable option for kitchens and bathrooms.
Sustainable Cabinetry
Sustainable cabinetry is made from eco-friendly materials such as bamboo, reclaimed wood, and formaldehyde-free plywood. These cabinets are designed to reduce environmental impact and improve indoor air quality.
Eco-Friendly Exterior Siding Options
Fiber Cement Siding
Fiber cement siding is made from a mixture of cement, sand, and cellulose fibers. It is durable, fire-resistant, and requires minimal maintenance. Fiber cement siding is also available in a range of colors and styles, making it a versatile and sustainable choice for building exteriors.
Recycled Metal Siding
Recycled metal siding is made from post-consumer metals such as aluminum and steel. It is a durable and low-maintenance option that can withstand harsh weather conditions. Using recycled metal helps reduce the demand for new raw materials and minimizes waste.
Green Building Materials for Structural Support
Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT)
Cross-laminated timber (CLT) is a type of engineered wood made by layering and gluing pieces of wood at right angles. CLT is strong, lightweight, and provides excellent thermal insulation. It is also a renewable material, making it a sustainable option for structural support.
Steel with Recycled Content
Steel is a common material for structural support in buildings. Using steel with recycled content helps reduce the environmental impact of construction. Recycled steel is just as strong and durable as new steel but requires less energy to produce.
Sustainable HVAC Systems
Geothermal Heating and Cooling
Geothermal heating and cooling systems use the stable temperature of the earth to regulate indoor temperatures. These systems are highly energy-efficient and can significantly reduce heating and cooling costs. Geothermal systems are also environmentally friendly, as they use renewable energy from the ground.
High-Efficiency Heat Pumps
High-efficiency heat pumps are designed to provide heating and cooling with minimal energy consumption. They use advanced technology to extract heat from the air or ground and transfer it indoors. High-efficiency heat pumps can reduce energy bills and improve indoor comfort.
Key Points Summary
- Eco-friendly concrete alternatives like fly ash and geopolymer concrete reduce carbon footprints.
- Green building materials for interiors, such as recycled glass countertops and sustainable cabinetry, enhance sustainability.
- Fiber cement and recycled metal siding provide durable and eco-friendly exterior options.
- Cross-laminated timber and recycled steel offer strong and sustainable structural support.
- Sustainable HVAC systems, including geothermal heating and high-efficiency heat pumps, improve energy efficiency.
The Role of Technology in Sustainable Construction
Building Information Modeling (BIM)
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a digital tool that allows architects, engineers, and builders to create and manage a building’s lifecycle. BIM helps optimize the use of green building materials, reduce waste, and improve project efficiency. By simulating different scenarios, BIM can help identify the most sustainable construction practices.
Smart Building Systems
Smart building systems use sensors and automation to optimize energy use, water consumption, and indoor air quality. These systems can monitor and adjust lighting, heating, cooling, and ventilation based on occupancy and environmental conditions. Implementing smart building systems can enhance the sustainability of a building and improve occupant comfort.
Eco-Friendly Building Materials for Water Management
Rainwater Harvesting Systems
Rainwater harvesting systems collect and store rainwater for use in irrigation, flushing toilets, and other non-potable applications. These systems reduce the demand for municipal water and help manage stormwater runoff. Using collected rainwater can significantly lower water bills and promote water conservation.
Greywater Recycling Systems
Greywater recycling systems treat and reuse water from sinks, showers, and laundry for non-potable uses such as irrigation and toilet flushing. These systems reduce water consumption and wastewater generation, making them an effective component of sustainable building design.
Green Building Materials for Energy Generation
Solar Panels
Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, providing a renewable and clean source of energy. Installing solar panels can reduce reliance on fossil fuels, lower energy bills, and contribute to a building’s overall sustainability. Advances in solar technology have made panels more efficient and affordable.
Wind Turbines
Small-scale wind turbines can generate electricity for buildings in windy areas. These turbines capture kinetic energy from the wind and convert it into electrical power. Wind energy is a renewable resource that can complement other green building materials and practices.
Sustainable Building Maintenance
Eco-Friendly Cleaning Products
Using eco-friendly cleaning products helps maintain indoor air quality and reduces environmental impact. These products are made from natural ingredients and are free from harmful chemicals. Choosing green cleaning products supports a healthier and more sustainable building environment.
Routine Maintenance and Inspections
Regular maintenance and inspections are essential for ensuring the longevity and performance of green building materials. Identifying and addressing issues early can prevent costly repairs and extend the life of building components. A proactive maintenance plan is key to sustaining the benefits of eco-friendly construction.
Key Points Summary
- Technology, such as Building Information Modeling (BIM) and smart building systems, enhances sustainable construction.
- Rainwater harvesting and greywater recycling systems promote water conservation and efficient water management.
- Solar panels and wind turbines provide renewable energy options for buildings.
- Eco-friendly cleaning products and routine maintenance support sustainable building practices.
- Regular inspections ensure the longevity and effectiveness of green building materials.
Challenges and Solutions in Using Green Building Materials
Common Challenges
While green building materials offer numerous benefits, there are challenges to their adoption. These challenges include higher upfront costs, limited availability, and a lack of awareness or understanding among builders and consumers. Additionally, some green materials may require specialized skills for installation and maintenance.
Overcoming Challenges
To overcome these challenges, it is important to educate stakeholders about the benefits of green building materials and practices. Government incentives, rebates, and certifications can also help offset costs and encourage adoption. Collaborating with suppliers and manufacturers can improve the availability of eco-friendly materials. Training programs for builders and contractors can ensure proper installation and maintenance of these materials.
Future Trends in Green Building Materials
Biodegradable Building Materials
The development of biodegradable building materials, such as mycelium and biodegradable plastics, is a promising trend in sustainable construction. These materials can decompose naturally, reducing waste and environmental impact. Biodegradable materials offer a sustainable alternative to traditional building materials.
Smart Materials
Smart materials are designed to respond to environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity changes. Examples include thermochromic windows that adjust their tint based on sunlight and self-healing concrete that repairs cracks automatically. Smart materials can enhance the performance and sustainability of buildings.
Conclusion
The Impact of Green Building Materials
Green building materials play a crucial role in creating sustainable and resilient buildings. They help reduce environmental impact, improve health and safety, and promote resource efficiency. By choosing eco-friendly materials, builders and homeowners can contribute to a more sustainable future.
The Path Forward
As technology and innovation continue to advance, the availability and performance of green building materials will improve. Education, incentives, and collaboration among stakeholders are key to overcoming challenges and driving the adoption of sustainable construction practices. Embracing green building materials is essential for creating a healthier and more sustainable built environment.
FAQs
- What are green building materials?
- Green building materials are eco-friendly construction materials that minimize environmental impact and promote sustainability throughout their lifecycle.
- Why are green building materials important?
- They reduce carbon footprints, conserve natural resources, and promote healthier indoor environments.
- What are some examples of green building materials?
- Examples include bamboo, reclaimed wood, hempcrete, mycelium, recycled glass, and low-VOC paints.
- Are green building materials more expensive?
- They may have higher upfront costs but often provide long-term savings through reduced energy and maintenance costs.
- What is LEED certification?
- LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) is a certification program that recognizes buildings for sustainable practices and the use of green building materials.
- How can I find green building materials?
- Look for materials with certifications such as LEED, ENERGY STAR, or other eco-labels. Suppliers specializing in sustainable products can also help.
- Can green building materials improve indoor air quality?
- Yes, many green materials, such as low-VOC paints and natural finishes, reduce indoor air pollution and promote healthier living spaces.
- What is passive solar design?
- Passive solar design involves orienting a building to maximize natural light and heat from the sun, reducing the need for artificial lighting and heating.
- What are the benefits of using recycled materials in construction?
- Using recycled materials reduces waste, conserves resources, and often has a lower environmental impact compared to new materials.
- How can technology support sustainable construction?
- Technologies like Building Information Modeling (BIM) and smart building systems optimize resource use, reduce waste, and improve building efficiency.

